Would you like to offer your employees new learning opportunities and optimize knowledge transfer...
Promote experiential learning with a LXP
Hidden deep in the vastness of the digital learning universe is a treasure trove of opportunities to transform learning in the company: Immerse yourself in the world of experiential learning in a corporate context! Discover an innovative approach that encourages employees to learn through hands-on experience and trying out new ideas and methods. Learn how organizations can foster a creative and innovative corporate culture through experiential learning and how you can leverage the entire learning cycle to achieve sustainable educational success.

What is experiential learning?
Experiential learning in the corporate context refers to an approach in which employees learn through hands-on experience and trying out new ideas and methods. Instead of traditional teaching methods, which are often based on theoretical knowledge, experiential learning emphasizes the active involvement of learners in the learning process rather than just passively absorbing information.
In experiential learning, employees are encouraged to hypothesize, try out different approaches and evaluate the results. This can be done through projects, simulations, case studies, prototyping or other hands-on activities. The advantage of this approach is that employees can gain direct experience and learn from mistakes, which often leads to a deeper understanding and a more sustainable acquisition of knowledge. In addition, experiential learning fosters a creative and innovative company culture where employees are encouraged to develop and test new ideas.
Some companies are also integrating experiential learning into their organizational structure by creating flexible work environments where employees have the freedom to try out new approaches and share their findings. This helps to create a learning organization that continuously evolves and adapts to keep pace with the ever-changing demands of the market.
Importance of experiential learning
In the process of experimental learning, employees can actively participate in their own knowledge acquisition. Through practical experience in the company or virtual environments, they discover new ways of learning. The integration of experiential learning into a LXP gives learners the opportunity to simulate real-life situations and expand their knowledge in innovative ways.
They find support in the targeted provision of information and assistance that promotes learning through discovery. Access to the bundled internal knowledge enables learners to deepen their understanding through independent work. By applying Kolb's learning cycle, managers can specifically support the experiential learning of their employees and thus promote sustainable educational success.
Here are some important aspects that underline the importance of experiential learning in the corporate context:
-
Practical experience: Experimental learning enables employees to learn directly in real or simulated work environments. This promotes a deeper understanding and faster application of what has been learned.
-
Mistakes as a learning opportunity: Experimentation allows employees to make mistakes from which they can learn. This culture of error fosters an environment where innovation and creativity can flourish without fear of failure.
-
Adaptability: The business world is constantly changing and companies must be able to adapt quickly to new requirements. Experimental learning enables employees to respond flexibly to change and develop new solutions.
-
Development of problem-solving skills: By experimenting with different approaches to solving problems, employees improve their ability to analyze, diagnose and solve problems in different situations.
-
Fostering innovation and creativity: Experimental learning encourages employees to develop new ideas and find innovative solutions to challenges. This contributes to continuous improvement and innovation in the company.
-
Teamwork and collaboration: Experimental learning can often be carried out in the form of team projects that promote collaboration and the exchange of ideas between employees. This strengthens team spirit and improves communication within the company.
-
Employee engagement and development: By giving their employees the opportunity to develop new skills and grow through experiential learning, companies increase employee engagement and retention.
The Kolb learning cycle and its
application in practice
- Concrete Experience: This is the first step of the learning cycle in which a person has a concrete experience or performs an activity.
-
Reflective Observation: After the experience, the person reflects on what happened and tries to derive patterns and meanings from the experience.
-
Abstract Conceptualization: In this phase, the person tries to understand the experience by placing it within larger concepts or theories and making connections.
-
Active experimentation: Finally, the person applies what they have learned in new situations and experiments with it to see how it works and whether it leads to new insights.
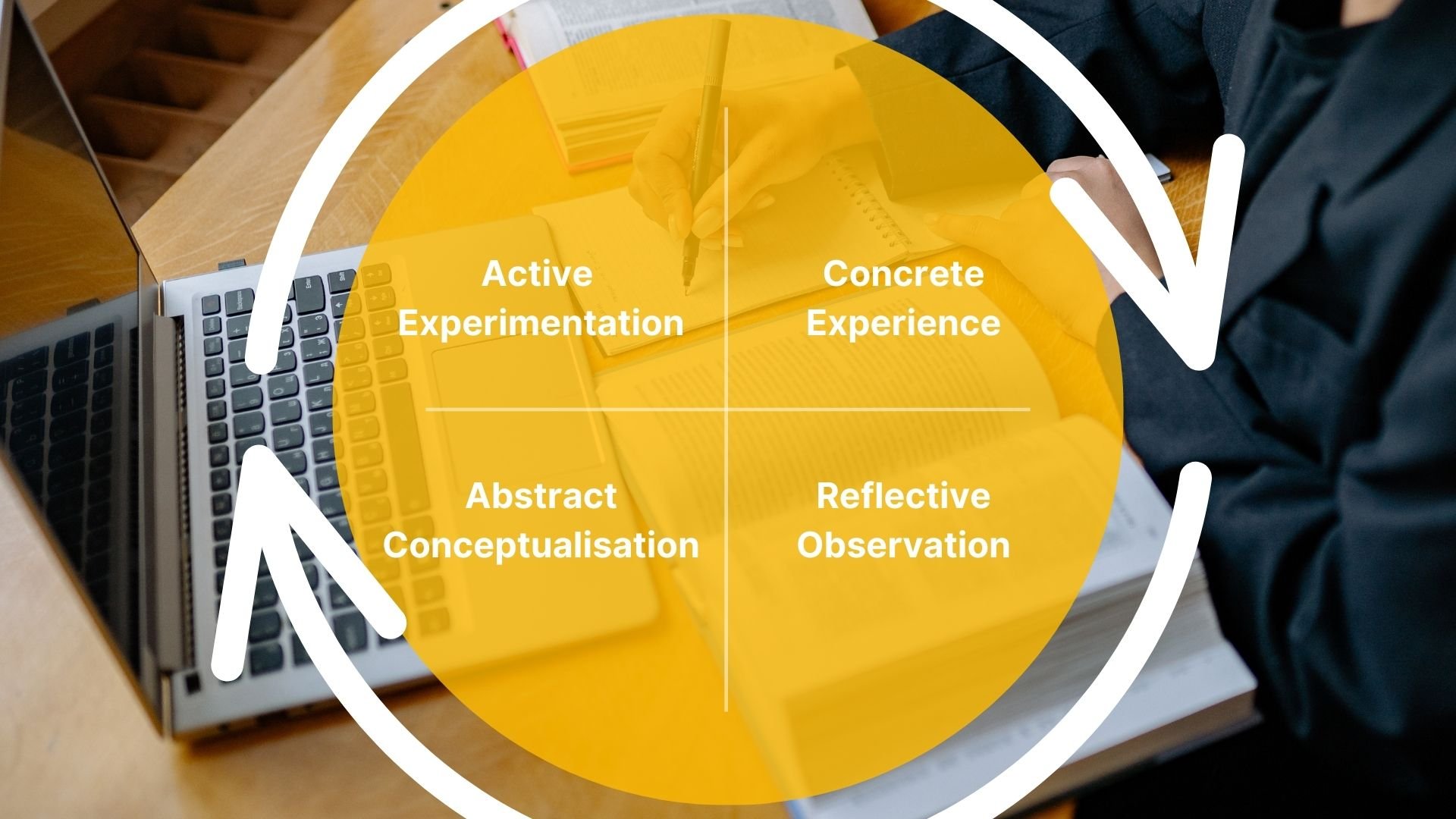
This cycle can be repeated continuously and represents a learning process. In business practice, Kolb's learning cycle model can be applied in various ways.
Companies can design training programs and development opportunities that take Kolb's learning cycle into account. For example, training could include practical exercises, reflection phases, theoretical input and the opportunity for participants to apply what they have learned in real-life situations.
Managers and trainers can use Kolb's learning cycle to provide feedback and support employees in their development. By asking questions that encourage reflection, they can encourage employees to learn from their experiences and try out new approaches.
Companies can also structure team projects that map the entire learning cycle. By working together in teams, employees can bring in different perspectives and learn from each other while sharing concrete experiences, reflecting, developing new concepts and experimenting.
Companies that promote an open error culture encourage employees to try out new ideas and experiment, even if mistakes are made in the process. By applying Kolb's learning cycle, employees can learn from mistakes, gain new insights and develop innovative solutions.
Experiential learning with a LXP:
definition and advantages
LXP stands for Learning Experience Platform. In the field of experiential learning, it offers a comprehensive opportunity to promote employees' discovery-based learning. By integrating real-life experiences into the learning process, learners can actively acquire knowledge. A LXP provides access to a wide range of information and supports learners in finding new insights on their own. It is a digital platform that supports companies in providing and managing learning experiences for their employees. The advantages lie in the interactivity and flexibility that make experimental learning in the virtual environment possible.
Definition: Experiential corporate learning with a LXP refers to the use of a digital learning platform to provide employees with the opportunity to learn through hands-on experiences, simulations, games and interactive activities. These platforms often provide personalized learning experiences and allow employees to learn at their own pace and focus on the areas that are most relevant to their professional development.
Advantages:
-
Flexibility and accessibility: With an LXP, employees can access learning content anytime, anywhere. This allows them to customize their learning experiences to their own schedules and learn from different devices.
-
Personalization: LXPs often offer personalized learning experiences that are tailored to employees' individual needs and learning styles. This helps to increase employee engagement and motivation.
-
Interactivity and engagement: By integrating interactive elements such as simulations, games and case studies, employees can be actively involved in the learning process, resulting in higher engagement and better knowledge retention.
-
Measurement and analysis: LXPs often offer features to measure and analyze learning success, such as progress tracking, tests and assessments. This allows companies to monitor learning success and continuously improve the effectiveness of their training programs.
-
Experiential learning: LXPs can support various forms of experiential learning, such as trying out new skills in simulated environments or applying knowledge in real-life scenarios. This enables employees to learn and develop their skills through hands-on experience.
Integration of experiential learning into the learning platform
Integrating experiential learning into a learning platform, be it an LXP or any other form of learning management system, requires careful planning and implementation. Here are some steps to successfully integrate experiential learning into a learning platform:
Start with a thorough analysis of your employees' learning goals and needs, as well as the types of skills they need to develop. Identify the areas where experiential learning could be particularly effective.
Identify the tools and resources to be used for experiential learning. This could include the integration of simulations, interactive case studies, virtual labs, gamification elements and other interactive activities.
Establish clear short- and long-term learning objectives to be achieved through experiential learning. This could include developing specific skills, solving specific problems or encouraging creative thinking.
Ensure that the learning platform provides a variety of curated learning content suitable for experiential learning. This could include training modules, videos, case studies, simulations, interactive games and other relevant resources.
Integrate interactive learning activities directly into the learning platform to encourage experiential learning. This could include embedding tests, quizzes, surveys, discussion forums, group projects and other collaborative activities.
Implement feedback mechanisms that allow learners to check and improve their understanding and skills. This could include the integration of automated assessments, peer feedback, trainer feedback and self-assessments.
Conduct regular evaluations to check the effectiveness of experiential learning and optimize the learning platform accordingly. Use data analysis and feedback from learners to make continuous improvements.
Provide staff with training and support on how to use the learning platform and the experiential learning activities. This could include training, manuals, tutorials and personal support.

Tips for promoting experimental learning among employees
Discovery learning can be invaluable in any area of education. To encourage experiential learning in your employees, it is helpful to provide them with opportunities to find new information in real-world ways. Experimentation and learning through hands-on experiences are important parts of an effective learning process. Here are some tips for encouraging experiential learning among employees:
-
Create an open error culture: Emphasize the importance of learning curves and that mistakes should be seen as part of the learning process. Employees should feel safe to try out new ideas and make mistakes without fear of negative consequences.
-
Provide time and resources for experimentation: Give employees the opportunity to spend time and resources on experimentation, be it through dedicated projects, workshops or regular "innovation time".
-
Enable a variety of learning methods: Ensure that employees have access to different learning methods, including practical exercises, simulations, case studies, group projects, discussions and mentoring.
-
Encourage self-reflection: Encourage employees to regularly reflect on their experiences, what they have learned and how they can improve. This could be achieved through feedback sessions or coaching.
-
Enable informal learning: Create a culture that supports informal learning, be it through informal conversations, learning communities, online forums or sharing best practices.
-
Integrate learning into work: Try to seamlessly integrate learning activities into daily work by linking them to real work tasks and supporting employees to directly apply what they have learned.
-
Encourage collaborative learning: Encourage employees to learn together and support each other, whether through peer mentoring, team projects or joint problem-solving activities.
-
Provide feedback and recognition: Give employees regular constructive feedback on their learning progress and successes and recognize their efforts and achievements.
-
Provide access to resources: Ensure that employees have access to the resources they need, be it training, tools, information or expert support, to achieve their learning goals.
-
Foster a learning organization: Create a culture where continuous learning and a willingness to try new ideas are encouraged, and where knowledge and experience are actively shared.
Conclusion: Effective experiential learning through the use of an LXP
Experiential learning offers a dynamic and effective method for developing employees in companies and continuously expanding their knowledge and skills. In contrast to traditional teaching methods, experiential learning emphasizes hands-on experiences and the active involvement of learners in the learning process. By experimenting with different approaches, gaining direct experience and learning from mistakes, employees can develop a deeper understanding and find innovative solutions to business challenges.
Integrating experiential learning into a learning experience platform (LXP) opens up new opportunities to promote employees' discovery learning and optimize the learning process. LXPs offer flexibility, personalization and interactivity that allow learners to expand their knowledge independently and apply it in innovative ways.
By applying Kolb's learning cycle, companies can specifically support the experiential learning of their employees and promote sustainable educational success. By promoting an open culture of error, offering different learning methods and facilitating informal learning, they create an environment in which employees can continuously grow and develop.
Ultimately, experiential learning is not only a means of knowledge transfer, but also a way to build a learning organization that continuously evolves and adapts to the changing demands of the market. By fostering a culture of experiential learning, organizations can help their employees reach their full potential and achieve long-term success.
Related topics


In times of a shortage of skilled workers and Generation Z, employers have to make an effort to...

Discover learning phases in which employees develop personally and professionally and find out how...
